Algarve is illustrated by a strong historic seismic activity with earthquakes that caused extensive damage in the building of the region. The earthquakes of 1722 and 1755 seriously a ected the Algarve coast, with high intensities (IX and X MCS).
Vila Real de Santo António is one of the most unique settings in the Algarve region. It is located on the site of the former border town of Santo António Arenilha, near the margin of the Guadiana River, which was completely devastated by the tsunami of 1755. The construction of the new village was part of the deployment of a central core, set up by the “Casa do Risco das Obras Públicas”.
The village constitutes a direct application of the urban model of the ‘Baixa Pombalina’, adapted to the scale and resources of the region. The orthogonal grid is implemented parallel to the river. The resulting blocks with a compact configuration are oriented in a North-South direction, dominated by longitudinal fronts, and with roofing and facade uniformly expressed.
The buildings follow the implementation of the “Pombaline” module, although with substantial reduction of the number of floors.
The buildings have two levels, with more sophisticated roof systems. They have orthogonal floor plans with great symmetry and geometric systematization, which is expressed especially in the configuration of the facades. The vertical di erence between levels is evident, reflecting the typology used for the solution of the openings, unlike what happens in the horizontal boundary, where there is uniformity of treatment, both in the internal organisation and between di erent housing units.
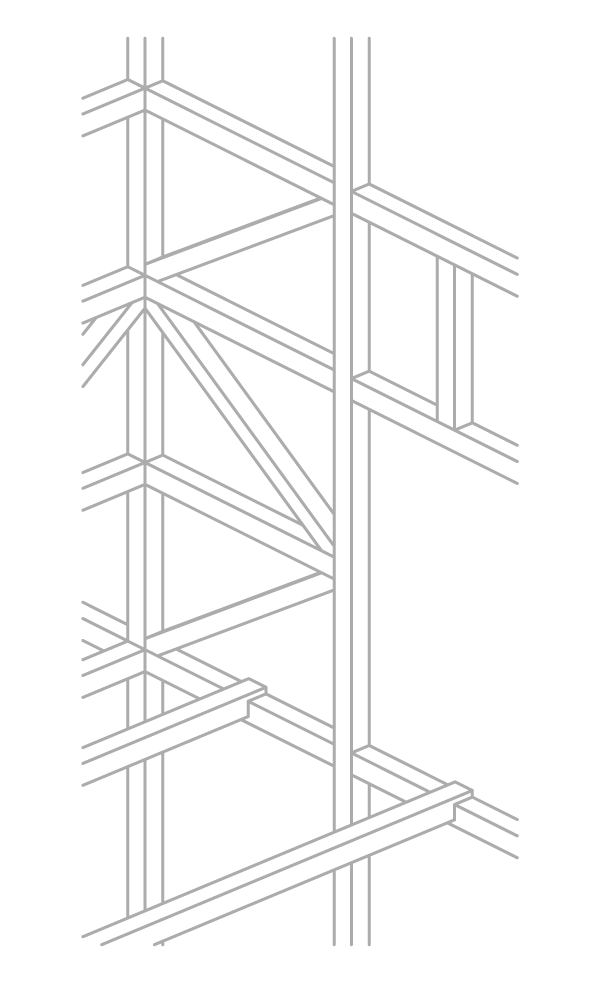
A significant part of the buildings used the “Pombaline” building system, with significant reduction of sections of the wooden cages and the corresponding stone masonry. The ground floor, entirely built in stone masonry resumes the strategy of using a structural base, using a roof system supported by arches. The upper floors use a frontal walls system, integrating, in several cases, the systematic application of metal tie-rods through the facade, principally to bind the floors of the upper levels.
Identified reinforcement elements
- Cage System
- Arch Vault
- Relieving Arch
- Horizontal Reinforcement
- Stone bench
- Reinforced Corner
- Reinforced Jambs
- Tie-rod